What is a CDN?
CDN is short for Content Delivery Network. This is a system of distributed servers (a network) that deliver pages and other web content to a user, based on the geographic locations of the user, the origin of the webpage and the content delivery server.
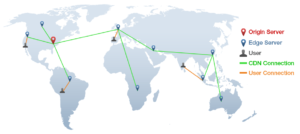
How Does This Work?
Servers nearest to the website visitor respond to the request. The CDN copies the pages of a website to a network of servers that are dispersed at geographically different locations, caching the contents of the page. When a user requests a webpage that is part of a CDN, the CDN will redirect the request from the originating site’s server in the CDN that is closest to the user and deliver the cached content. CDN’s will also communicate with the originating server to deliver any content that has not been previously cached.
The process of bouncing through CDN’s is nearly transparent to the user. The only way a user would know if a CDN has been accessed is if the delivered URL is different than the URL that has been requested.
Why Do We Need A CDN?
When delivering large scale websites to a global audience, CDNs can reduce latency, accelerate site load times, reduce bandwidth consumption secure applications & even block data scrappers & other forms of spammers hitting your server.
Final Thoughts
CDN’s are used for B2B interactions an in serving content to consumers. Today as more aspects of daily life more online, organisations use CDN to accelerate static content, dynamic content, mobile content, e-commerce transactions, video, voice, games and so on.
